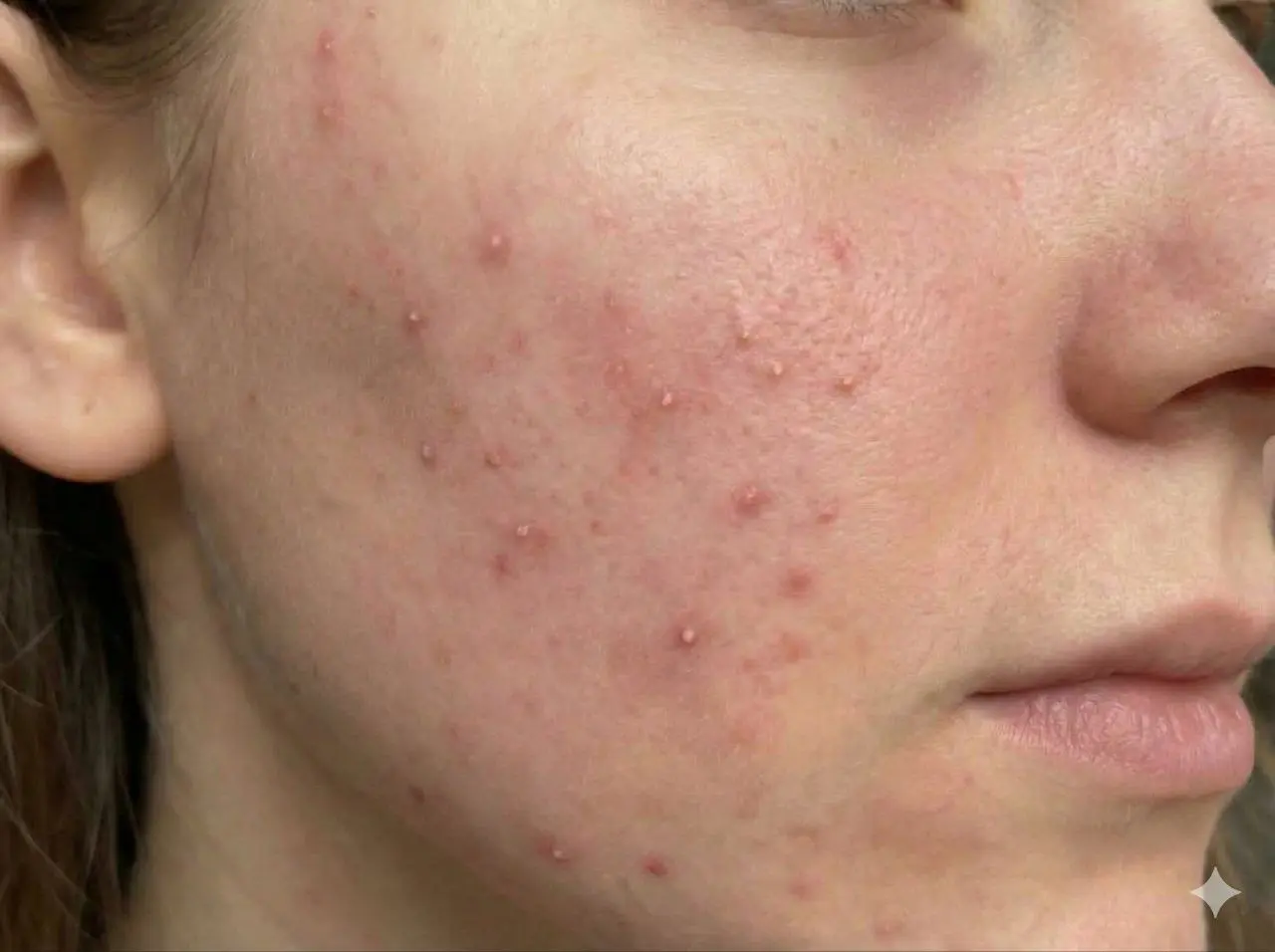
Acne vulgaris
June 8, 2025 by SkinGenius
Overview
Acne vulgaris is a common skin condition that primarily affects teenagers and young adults, although it can occur at any age. It is characterized by the presence of pimples, blackheads, and cysts, primarily on the face, back, and shoulders. Acne occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to inflammation and infection.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of acne vulgaris is multifactorial. Hormonal changes, particularly during puberty, can increase oil production in the skin. Other contributing factors include genetics, certain medications, and dietary habits. Stress and exposure to certain environmental factors may also worsen acne.
Symptoms
Symptoms of acne vulgaris include the appearance of various types of lesions such as whiteheads, blackheads, papules, pustules, and cysts. These can be painful and may lead to scarring if not treated properly. Acne can also cause emotional distress and affect self-esteem.
Contagiousness
Acne vulgaris is not contagious. It cannot be spread from person to person through direct contact or sharing personal items.
Diagnosis Methods
Diagnosis of acne vulgaris is typically made through a physical examination of the skin. A dermatologist may ask about the patient's medical history, lifestyle, and any medications being taken. In some cases, additional tests may be conducted to rule out other skin conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for acne vulgaris varies based on severity. Over-the-counter topical treatments containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid can be effective for mild cases. For moderate to severe acne, prescription medications such as topical retinoids, antibiotics, or oral contraceptives for females may be recommended. In some cases, procedures like chemical peels or laser therapy may be used.
Prognosis and Recovery
The prognosis for acne vulgaris is generally good. With appropriate treatment, most individuals see significant improvement. However, some may experience persistent acne or scarring. Early intervention can help minimize long-term effects.
When to Seek Medical Attention
You should seek medical attention if your acne is severe, persistent, or causing significant emotional distress. Additionally, if you notice signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus, it is important to consult a healthcare professional.
Self-care Tips and Prevention
- Wash your face gently twice a day with a mild cleanser to remove excess oil and dirt without irritating your skin.
- Avoid picking or squeezing acne lesions, as this can lead to scarring and worsen inflammation.
- Use non-comedogenic skincare and makeup products, which are specifically formulated not to clog pores.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting sugary and greasy foods that may trigger breakouts.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day to help keep your skin healthy.